In a special issue of the magazine Ethnobotany Research and Applications A publication by our scientists from the Department of Plant Conservation Biology titled, "The Plant Conservation Biology. People and plants - close relationships at the crossroads of the Silk Roads: the case of Tajikistan https://ethnobotanyjournal.org/index.php/era/article/view/5783.
This work analyzes the spatial relationships between human populations, livestock and wild useful plants in Tajikistan, an area along the intersection of the Silk Road. The goal of the study was to understand how the distribution of wild utilitarian plant species correlates with the presence of humans and livestock.
The study was based on statistical modeling to assess spatial relationships between human populations and 1,823 wild plant species identified as having utilitarian properties. The analyses conducted took into account various factors that can affect the distribution of human populations, such as bioclimatic conditions and plant use categories. The analysis reveals that not only utilitarian plants significantly affect the distribution of humans, but also their specific utilitarian groups, such as food and medicinal plants. Undoubtedly, the most important observation is that these predictors show much greater importance to the model than the predictors usually typified as most important in determining the location of human settlement. Examples include the relatively low importance of altitude, amount of precipitation or total flora richness, despite the fact that there is a significant relationship between the above factors and the size of population distribution. The results therefore indicate that the abundance of useful plants was more important to early settlement than previously thought.
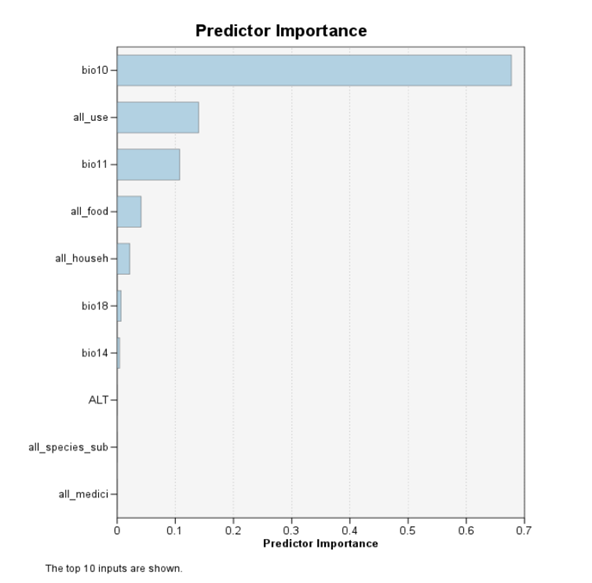 Fig. 1. Significance of individual predictors for the human population size distribution model. bio10 - average temperature of the warmest quarter, all_use - all useful plants, bio11 - average temperature of the coldest quarter, all_food - food plants, all_househ - plants used in the household, bio18 - precipitation of the warmest quarter, bio14 = precipitation of the driest month, ALT - altitude above sea level, all_species_sub - all plant species, all_medici - medicinal plants.
Fig. 1. Significance of individual predictors for the human population size distribution model. bio10 - average temperature of the warmest quarter, all_use - all useful plants, bio11 - average temperature of the coldest quarter, all_food - food plants, all_househ - plants used in the household, bio18 - precipitation of the warmest quarter, bio14 = precipitation of the driest month, ALT - altitude above sea level, all_species_sub - all plant species, all_medici - medicinal plants.
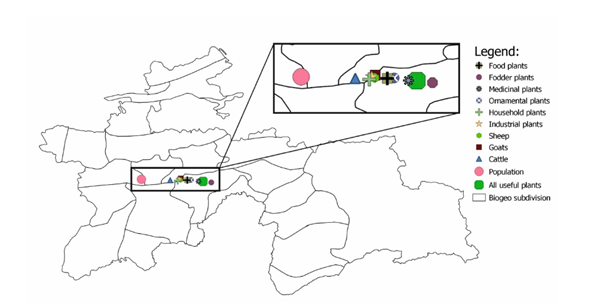
Fig. 2. Spatial means of incidence of analyzed variables
post
post
2024-08-26 13:01:17


